A fraction's value is not altered if both the numerator and denominator are multiplied by the same number.
Example:
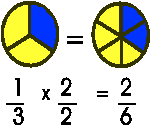
In the pie chart above, the pie on the left of the equal sign is dividied into three equal parts and the pie on the right is divided into six equal parts. The section colored blue is 1/3 of the whole pie on the left of the equal sign which is equivalent to 2/6 of the pie on the right of the equal sign.
Example:
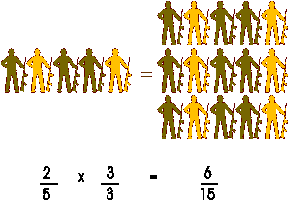
In the marching men illustration, there are 5 marching men on the left of the equal sign and 15 men on the right of the equal sign. On the left, there are 2 men in gold uniforms, thus 2/5 wear gold. On the right, there are 6 men in gold uniforms, thus 6/15 wear gold. The fraction of men in gold uniforms is the same on both sides of the equal sign. If we multiply 2/5 by 3/3, we get 6/15.
Example:
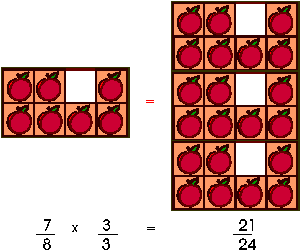
In the apples example, a box contains 8 apples, one is missing so we have 7 apples left, thus we have 7/8 of a box. On the right of the equal sign, there are 3 boxes that could contain 24 apples. Three apples are missing so we have 21 apples left, thus 21/24 of the apples are present. The fraction of apples present is the same on both sides of the equal sign. If we multiply 7/8 by 3/3, we get 21/24.
Property 2 - Reduction
A fraction's value is not altered if both the numerator and denominator are divided by the same number.You will notice that Property 2 is the opposite or inverse of Property 1.
Example:

This pie chart example is the inverse of Property 1, where 2/6 can be reduced to 1/3 without changing the value of the fraction.
Example:
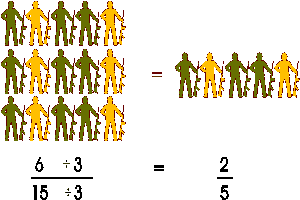
This marching men illustration again shows the inverse of Property 1, where 6/15 is equal to 2/5.
Example:
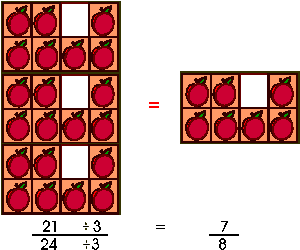
This apple example also shows the inverse of Property 1,
in which 21/24 apples are equal to 7/8.